What does ‘Data Science’ mean to you? Why did you pick Data Science?
☞ Data science is a multidisciplinary field that uses scientific methods, algorithms, processes, and systems to extract knowledge and insights from structured and unstructured data or generate new models.
Since this is a highly personal question, I will just list my (the author) own reasons. Nonetheless - make sure you have a crystal clear answer for this question.
“Well, thanks for asking. The main reason I fell in love with data science is because…”
Why? It’s so simple. I like programming, I love statistics, like, pure brain tickle. And, I promised my parents that I would be an engineer, and I promised my friends that I would build things… Long term, I wanna get good enough at ML to use for good. It has so many right tail applications. Where should we mine, autonomous drones. What about, how do we solve poverty. ML can literally solve impossible problems; image f*cking generation. Real chatbot intelligence. Why can’t we solve poverty?
- Joma tech video
- data science was originally called…
- This is your opportunity to demonstrate genuine enthusiasm and passion to the interviewer, and call upon personal anecdotes.
- what got you interested?
If you don’t have basic understanding of ‘data’ - please read act II
Everyone’s talking about AI these days. Can you tell me: what Artificial Intelligence actually means?
☞ AI describes anything created to perform a task which usually requires human intelligence.
- (We are trying to match if not exceed human intelligence)
- Furthermore, Machine Learning describes a subclass of algorithms to solve problems that cannot be explicitly programmed by humans.
Q4) (You are passed a piece of paper) How would you classify AI vs. Machine Learning?
AI vs Machine Learning | IBM ![[ml-ai-venn.svg | center | 400]]
(A) What is the difference between narrow and wide AI?
Narrow AI
- Designed to perform a specific task
- It operates under a limited, predefined range or set of parameters
- For example: chatbots, recommendation systems, image recognition
Wide AI
- Agnostic to any specific task, simply ‘intelligent’ like a human being, able to perform any task and apply its intelligence across any domain.
- Able to learn from experience, and adapt to new information through transfer learning.
(A) What is artificial general intelligence (AGI)?
Also known as ‘Wide AI’.
Q9.1) What is domain knowledge and why is it important in data science?
Q9.2) What are some of your areas of domain expertise?
What is exploratory data analysis?
☞
Why is it crucial to actually ‘look at’ your data; whether this be the raw data in rows and columns, or through graphs?
-
The brain itself is a model; and is programmed to recognise certain patterns extremely effectively (there is a reason the architecture of neural networks parallels on the structure of our brains) (Show a sick picture (midjourney) of like idk a red box around a mother’s face) (threat)
-
To spot anomalies and do bare minimum verification of the data’s legitimacy - so many errors avoided if you could just.
Q5) Please tell me about a time when you have used Machine Learning in your own life.
Make sure you keep a personal list, in order of interesting-ness (you can’t talk about all of them)
- Daily routines - perhaps you made a script to make your life easier
- Real Projects (uni, jobs, hackathons)
- Food classifier
- University assignments
- Yes/No
- Food thing
- Hagen’s Organics
###### What does it mean to 'model' something
WIth machine learning and deep learning inevitably comes mathematical language
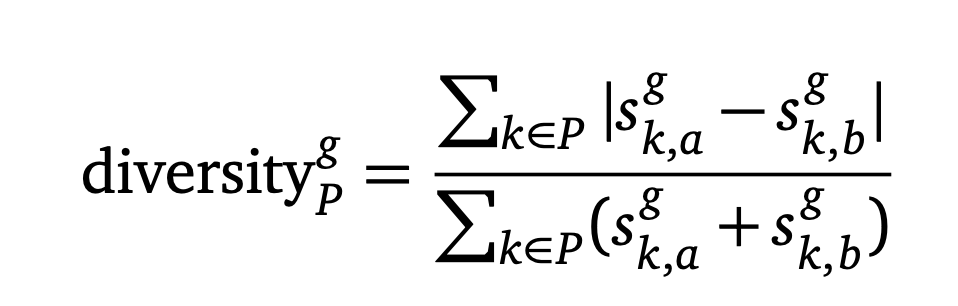
If you don’t understand this, it’s not becuase you don’t understand math. It’s because you don’t understand how to read math.
What are the learning paradigms of ML
Machine Learning
│
├── Supervised Learning
│ ├── Classification (task of identifying category) (could also be predition)
│ └── Prediction (Regression) (task of predicting continuous values)
│
├── Unsupervised Learning
│ ├── Clustering
│ └── Dimensionality Reduction
│
├── Semisupervised/Reinforcement Learning
│
└── Miscellaneous
├── Generative AI
├── Active Learning
├── Ensemble Methods
└── … (other advanced techniques)
⁂ Note, these are just ways to describe ML systems, they do not necessarily fall neatly into each of these categories! For example: 2.20 Recommender Systems.
Supervised learning: Supervised Machine Learning refers to a type of machine learning where the algorithm is trained on a labeled dataset, which means the algorithm is provided with input-output pairs. The goal is to learn a mapping from inputs to outputs and make predictions on new, unseen data based on this learned mapping.
Unsupervised learning does not have (or need) any labeled outputs, so its goal is to infer the natural structure present within a set of data points.
Semi-supervised learning aims to label unlabeled data points using knowledge learned from a small number of labeled data points.
Reinforcement learning
What is supervised ML
What is classification? Can you name some examples?
Classification
- The art of classifying a bunch of objects into two or more categories.
Examples
-
Is this email spam or not spam (
true/false) -
Is this loan application good or bad (
1/0) -
Is this animal in this picture a dog, cat, or bird? (
a, b, c) -
Who is in this photo? (Facial detection)
-
Which letter is in this photo? (
a-z) -
Is this wine good or bad? (
1/0) -
Is this stock going up or down (
1/0) -
Medicine
-
Marketing
-
Sales
-
Economics
-
Social sciences
For tasks such as:
- Disease diagnosis
- Predicting customer churn
↳ What is prediction/regression
Prediction/Regression
- Predicts an attribute associated with an object
- Yields continuous values instead of categorical variables
Examples
- Stock price forecasting
- Weather forecasting
What is unsupervised learning
Clustering
- Customer Segmentation
The Current ML Taxonomy
- Computer Vision
- NLP
What is active learning?
some models are heuristiic, some ,…
Q1) Let’s say you want to make a model. What are the general steps you take?
First principles
The holistic machine learning recipe (chant this every night before you go to sleep):
- Acquire data
- Clean and prepare data into good features
- Split the data into training and testing set
- Pick a model (the fun part)
- Traditional Statistical models: linear regression, logistic regression
- ML Model: decision tree, kNN
- Deep Learning: cNN{algorithm which assigns weight to features, takes input, automatically takes additional features - helpful for images or Natural language where manual feature engineering}
- Train: train data is fed into algorithm to build model
Training
In machine learning, training the algorithm, or learning, is formally the process of estimating the parameters of the model from the data
- Test: test data used to evaluate the accurate or error of the model
How to select different models?
- Comparing, validating and choosing parameters and models
- Improve model accuracy via parameter tuning
Dimensionality Reduction ≠ PCA
- Reducing the number of random variables (features, columns) to consider
- Increases model efficiency
Pre-processing
- Feature extraction and normalization
Raw input data -> usable with ML Algorithms
What is Machine Learning?
☞ Machine Learning: How to teach a computer a task, without explicitly programming it to perform said task. Instead, feed data into an algorithm to gradually improve outcomes through experience.
What two different types of tasks do all machine learning models do?
☞ Classification of present data into categories
☞ Prediction about the future
regression?
Explain the broad types of structured data, and give an example of each.
Data Types
│
├── Numerical
│ ├── Continuous
│ │ └── Can take any value within a range; suitable for measurements.
│ └── Discrete
│ └── Countable values; suitable for counting occurrences.
│
├── Categorical
│ ├── Nominal
│ │ └── No inherent order; labels or names for categorizing data.
│ └── Ordinal
│ └── Ordered categories; not evenly spaced.
│
└── Boolean
└── Binary values (True/False); commonly used in binary decisions.
-
Continuous Data: These are measurements and can take any value within a range. They are often used in regression models where you predict a continuous outcome, like house prices or temperatures.
-
Discrete Data: These are countable items, often integers. They are used in scenarios where you count occurrences, like the number of sales transactions.
-
Categorical Data: These are types that categorize. Nominal data has no order (like car brands), while ordinal data has a clear ordering (like satisfaction levels). They are frequently used in classification problems.
-
Boolean Data: This is a binary data type (True/False) and is commonly used in binary classification tasks, like spam detection in emails.
Then of course there are things that are more unstructured; dates, images, text